
Nearly six in 10 consumers in Germany and Austria believe meat consumption is too high, but less than half think these foods are bad for the climate and plan to reduce their intake of animal products, according to new surveys. Even fewer want to eat more plant-based alternatives in the next two years, but there are indications of support for cultivated meat.
Despite being Europe’s largest plant-based market, only 30% of Germans want to up their intake of vegan meat analogues, and just 46% want to eat fewer animal products over the next two years. This is ditto for neighbouring Austria too, despite 59% of consumers (and 58% in Germany) thinking meat consumption is too high.
This is according to two surveys by YouGov on behalf of the Good Food Institute (GFI) Europe, which covered over 1,000 Austrian and more than 2,000 German consumers. Ivo Rzegotta, senior public affairs manager for Germany at GFI Europe, argues that the results are still positive. “Overall, the market for plant-based foods in Germany has expanded by 42% since 2020, solidifying the country’s position as a leader in embracing plant-based foods in Europe,” he told Green Queen.
“The fact that 30% of respondents are keen to further increase their consumption of plant-based meat and dairy products is a promising indicator, especially considering the already significant portion of the population favouring plant-based options.”
The polls revealed that 57% of the former and 51% of the latter don’t think meat and animal products are a major problem for the climate – animal agriculture emits twice as many emissions as plant-based foods, with meat accounting for 60% of the entire food system’s carbon footprint.
“People choose alternative proteins for various reasons, including concerns about climate change. However, health and animal welfare are often cited as primary motivations for reducing meat consumption, in line with existing consumer research,” said Rzegotta. “The science is clear on the role of industrial farming in driving climate change and it’s up to policymakers to facilitate the transition to more sustainable food production.”
There is some optimism around cultivated meat too, with 42% of Austrians and 47% of Germans willing to try these novel proteins at least once – a separate in-market survey published last week showed that eating cultivated meat significantly boosts people’s acceptance of it, with a majority indicating they’d buy it again.
Germans and Austrians split on plant-based foods
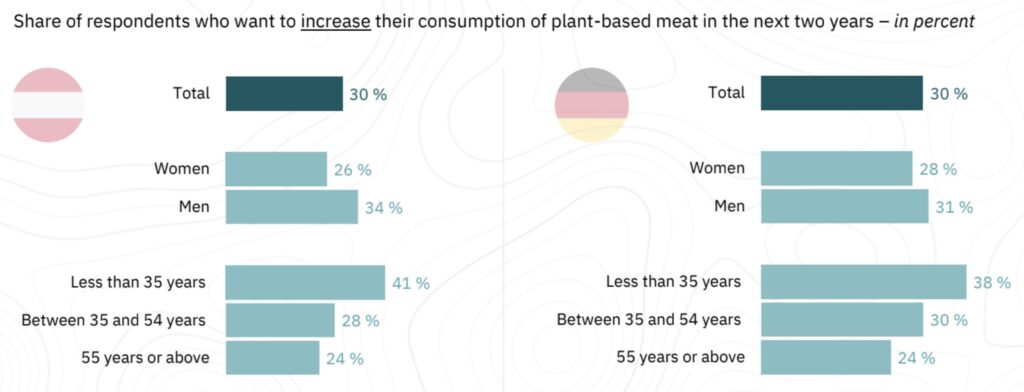
In both countries, the interest in upping plant-based meat consumption was slightly higher in men than women, and reduced proportionally with age, with 41% of Austrians and 38% of Germans aged 35 or under planning on eating more meat alternatives, versus 24% for over-55s.
The results are similar for plant-based dairy consumption too, with 28% of Austrians and 27% of Germans wanting to consume more of these foods in the next two years, and the same trend in age demographics. However, men are more interested in doing so in Austria, while the opposite is true in Germany. Overall, just under half of respondents in Austria (47%) and Germany (49%) believe that alternatives to animal products are needed.
That said, there is stronger support for policies to cut the VAT on plant-based milk, with 60% of Austrian consumers agreeing it should come down from 20% to the standard 10% applied to cow’s milk, and 62% of Germans thinking policymakers should reduce the levy from 19% to 7%.
“Germany and Austria stand out in Europe for imposing a higher tax rate on plant-based dairy compared to animal-based dairy, which undoubtedly impacts consumption patterns,” explained Rzegotta. “Establishing a level playing field in terms of taxation is crucial to facilitate consumer choice in favour of plant-based options. By addressing disparities in pricing, policymakers can encourage broader adoption of plant-based dairy products, aligning with consumer preferences and advancing sustainability goals.”
Both countries also have 53% of consumers expressing support for policies that would allow farmers to produce more plant-based foods, which is something the German government is already doing. But Austrians are evenly split on whether lawmakers should increase the range of vegan food in public canteens, while 44% believe governments should support research into foods that can replace animal-derived foods. In Germany, support for both these policy moves lies at 47%.
If deemed to be safe, cultivated meat should be a consumer choice
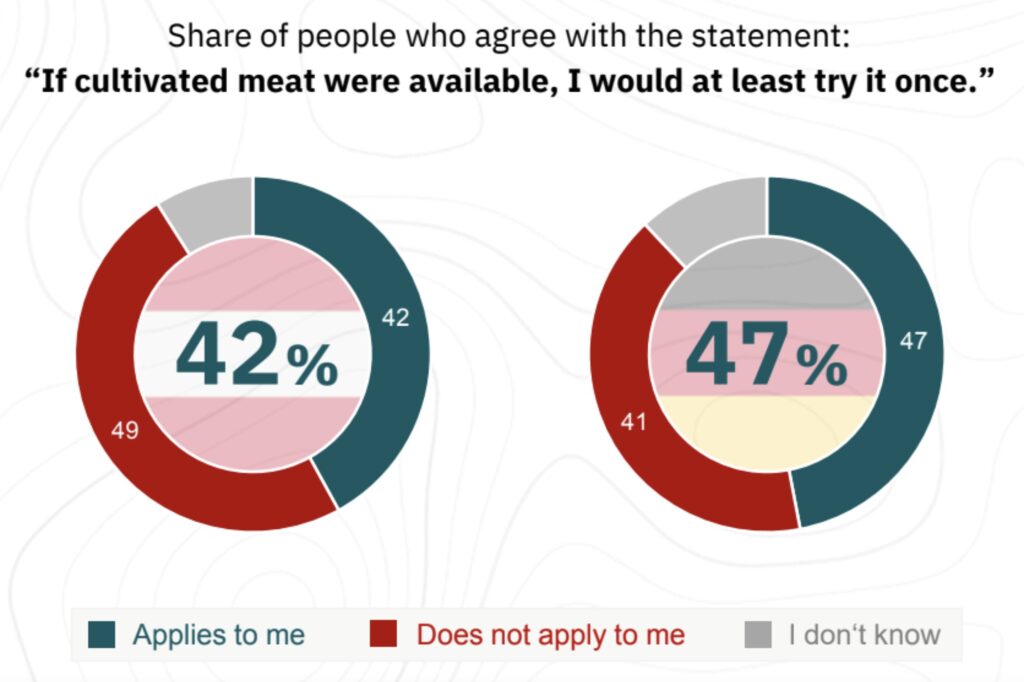
Acceptance for cultivated meat is slightly more encouraging in both Austria and Germany, where 59% and 53% of consumers are familiar with these foods, respectively. In fact, 47% of Germans said they’re willing to try cultivated meat once, as did 42% of Austrians. Here, too, men expressed a greater interest in both countries, and for flexitarians, this number rose to 58% in Germany and 58% in Austria.
Interestingly, though, only about a third of consumers in the two nations said cultivated meat appealed more to them than plant-based options. “There will always be a share of consumers who don’t find plant-based meat appealing for a number of reasons. If 34% of respondents say that cultivated meat is more appealing to them than the current generation of plant-based options, this suggests that this new option could reach a significant group of people who aren’t interested in plant-based meat,” noted Rzegotta. “Overall, the fact that nearly half of consumers in both countries are willing to try cultivated meat – a novel product unfamiliar to many and not yet available in Europe – highlights a promising market demand.
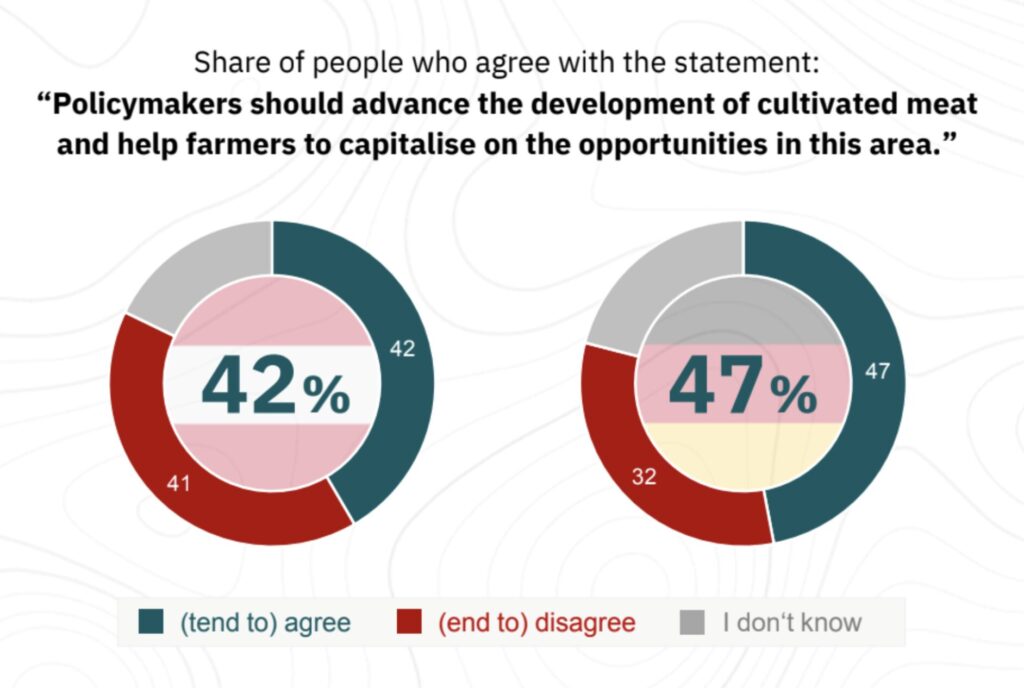
Two-thirds of respondents from both countries believe if cultivated meat does come to market, it should be produced locally to benefit the economy. When it comes to public investment, 42% of Austrians and 47% of Germans think governments should advance the development of cultivated meat and help farmers capitalise on the opportunities.
This industry has been the subject of intense debate in policy circles lately. Whereas the discourse in the US has stemmed from Florida’s impending ban, in Europe, Italy already became the first country to prohibit the sale of cultivated meat, with France and Romania attempting to do so too. In January, a delegation led by Austria, Italy and France brought a note to the EU’s Agriculture and Fisheries Council meeting, raising concerns about the bloc’s cultivated meat policies and calling for an overhaul to the regulatory framework, as well as a ban of meat-related terms.
While it was eventually tabled, the note was presented by Austria’s agriculture minister, Norbert Totschnig, but the country’s health ministry – which is responsible for food safety – said the move did not reflect the government’s position. Judging from the YouGov polls, it did not reflect the public’s position either.
Seven in 10 Austrians say only food safety and consumer protection should be decisive for the authorisation of cultivated meat, which 63% think should happen if the food safety authority deems it safe and nutritious. For 64%, the decision to clear the sale of these products should be independent of the food industry’s economic interests, and 66% feel policymakers should adhere closely to the food regulators’ recommendations when deciding to authorise cultivated meat.
Similarly, in Germany, 69% agree with that statement about food safety and consumer protection being the only decisive factors, 65% think a regulator’s assessment of safety should be enough for authorisation, and 66% believe politicians should stick to that advice. Meanwhile, 61% think the decision shouldn’t rely on the economic interests of the food sector.
In other words, if the country’s food safety authority greenlights cultivated meat, that’s the only decision the government should and must take into account. “Cultivated meat must go through one of the world’s most robust food regulatory processes before it will be available in the EU. Once it’s been approved, Germans and Austrians believe it should be up to consumers themselves to decide whether or not to eat cultivated meat,” said Seth Roberts, policy manager at GFI Europe.
“In the wake of the Italian ban, policymakers should note that people who responded to this survey – regardless of their political views – are increasingly aware of the economic opportunities offered by cultivated meat and are more interested in consumer choice than ideological debates.”
The post Germans & Austrians Believe Meat Consumption is Too High, But Less Than Half Think It’s Bad for the Climate appeared first on Green Queen.
This post was originally published on Green Queen.