
The Atlantic‘s Jeffrey Goldberg (3/24/25) complained “the group was transmitting information to someone not authorized to receive it”—an odd criticism for a journalist to make about government officials.
The Houthis, formally known as Ansar Allah, are the de facto government in northwest Yemen. The group began as a religious movement among the Zaydis, an idiosyncratic branch of Shia Islam, before taking a political-military turn in the 2000s. Since 2014, Ansar Allah has been a powerful faction in the country’s civil war, fighting against the Republic of Yemen, the weak but Saudi-backed internationally recognized government. With the war on hold since a 2022 ceasefire agreement, the Houthis now control the capital city of Sanaa, and govern the majority of Yemen’s population.
Beginning on March 15, the US military began an operation that has killed dozens in Yemen and injured over a hundred, including women and children, in which Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth frankly acknowledged the leveling of a civilian building.
US planning for the operation was revealed in articles by the Atlantic‘s Jeffrey Goldberg (3/24/25, 3/26/25), which disclosed that the journalist had been inadvertently added to a Signal group chat that top administration officials were using to discuss bombing plans—an inclusion that was not noticed by any of the intended participants. This prompted a furor in establishment papers like the New York Times and Washington Post, centering on the Trump administration’s use of an insecure messaging app to discuss classified matters.
While leading newspapers were not wrong to skewer the Trump administration for the use of a commercial messaging app to communicate confidential information—which, it should be remembered, allows officials to illegally destroy records of their deliberations (New York Times, 3/27/25)—the focus on Washington palace intrigue over the bombing of women and children is a stark reminder of corporate media priorities.
‘It’s now collapsed’
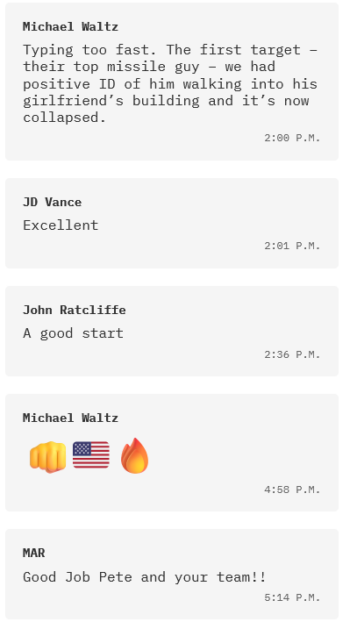
The part of the Trump administration group chat where they discuss the actual bombing needed no comment, according to the New York Times (3/26/25).
Since news of the Signal leak broke, the Times has published at least three dozen stories and opinion pieces focusing on the scandal. One of those many pieces was an annotated transcript of the Signal chat (3/25/25). Most messages in the chat featured explanatory notes from journalists, some messages with multiple notes. One message from national security adviser Michael Waltz the Times chose not to annotate: “The first target—their top missile guy—we had positive ID of him walking into his girlfriend’s building and it’s now collapsed.”
The “collapsed” building in question was bombed by the United States, killing at least 13 civilians, according to the Yemen Data Project. This is a war crime. While alternative media outlets have been quick to call these strikes out for what they are (e.g., Drop Site, 3/16/25; Truthout, 3/26/25; Democracy Now!, 3/26/25), the Times and the Washington Post chose not to go into questions of international law.
Amidst the dozens of stories on the Signal scandal, the Times published five stories focused on the strikes (3/15/25, 3/16/25, 3/19/25, 3/26/25, 3/27/25). None of these stories entertain the possibility of US strikes violating international law. Only one story (3/16/25) made mention of the phrase “war crime,” which was in a final paragraph quote from Hezbollah, with the group described by the Times as “another armed proxy for Iran in the region.”
The only mentions of children or “civilian” casualties were moderated by innuendo. The unfair convention of citing the “Hamas-run” health ministry—a formulation that deliberately downplays the death and destruction caused by US weaponry—has extended to Yemen, with both the Times (3/16/25, 3/19/25) and the Post (3/15/25) citing the “Houthi-run Health Ministry in Yemen” for casualty figures.
‘No credible reports’

The Washington Post‘s Missy Ryan (3/17/25) doesn’t question the Pentagon’s claim that there were “no credible reports of civilian deaths” after the attack on Yemen.
The Washington Post seemed similarly unable to bring international law into their reporting. The furthest the Post (3/15/25) was willing to go was relaying that the Houthis “claimed the strikes targeted residential areas and targeted civilians.” In the Post’s March 17 story on the US offensive, the only mention of civilian deaths was US Lt. Gen. Alexus Grynkewich’s claim that “despite Houthi assertions, there had been no credible reports of civilian deaths in the ongoing US strikes.”
Even Ishaan Tharoor (Washington Post, 3/26/25), whose column on the Yemen strikes was both more humane and more geopolitically realistic than anything else published by the Post, chose not to bring in any mention of international law.
The fact is, unnecessarily bombing a civilian building, with civilians inside, is a war crime. A civilian building is any building not immediately being used for military purposes. Even if by some interpretation, a military officer’s girlfriend’s building could be construed as a military target, the attacker is responsible for ensuring that any civilian losses are not excessive compared to military gain (the “proportionality” rule), and ensuring that “all feasible precautions must be taken to avoid, and in any event to minimize, incidental loss of civilian life, injury to civilians and damage to civilian objects.”
In this case, the “military” nature of the target is dubious at best. Further, the Houthis had not attacked US ships since December, before Trump’s inauguration (Responsible Statecraft, 3/21/25). When the Houthis attempted to respond to the recent airstrikes, a US military officer mocked the Houthis’ “level of incompetence,” claiming their retaliatory missile fire “missed by a hundred miles” (New York Times, 3/19/25). In other words, Houthi missiles are not such an imminent threat that killing over a dozen Yemeni civilians might be “proportional” to the military gain of killing their top missileer.
Finally, “all feasible precautions” were not taken to protect civilian life. Based on Waltz’s message, the military was tracking this officer, and chose to kill him only once he entered a building with civilians inside.
As the Times itself (1/16/23) has reported, “it is considered a war crime to deliberately or recklessly attack civilian populations.” The Washington Post editorial board (7/2/23) agreed, citing “large-scale destruction of civilian infrastructure” and “methodical violence against…noncombatants” as violations of international law. But these confident media assertions are in reference to Russia, an official enemy of the United States.
The strike against the “missile guy” is just one example of the indiscriminate bombing with which the US punishes Yemen. This recent offensive by the United States has destroyed plenty of residences, and airstrikes have hit a Saada cancer hospital twice (Drop Site, 3/16/25; Cradle, 3/26/25).
‘A more aggressive campaign’

After the US bombs an apartment building, killing more than a dozen civilians, the New York Times (3/16/25) turns to sources who declare that a “more aggressive” approach is needed.
Houthi-controlled Yemen sits on one side of the Bab-el-Mandeb, a narrow strait between the Arabian Peninsula and Africa that is a choke point for shipping between Asia and Europe. The Houthis announced in October 2023 that in opposition to the war on Gaza, they would use their strategic position to attack ships “linked to Israel” (Al Jazeera, 12/19/23). The Houthis have succeeded in disrupting Red Sea trade to the point that Israel’s only port on the Red Sea, the Port of Eilat, was forced to declare bankruptcy (Middle East Monitor, 7/19/24). As revealed by the Signal chat leak, the main motivation for the new air campaign on Yemen was to “send a message” and reopen the shipping lanes (New York Times, 3/25/25).
As US bombs fell on Yemen, the New York Times indulged in a variety of foreign policy reporting cliches. A day after the strikes began, the Times (3/16/25) took a survey of what should be done about the supposed threat the Houthis posed in the Middle East:
Some military analysts and former American commanders said on Sunday that a more aggressive campaign against the Houthis, particularly against Houthi leadership, was necessary to degrade the group’s ability to threaten international shipping.
The only voices the Times offered as a counterpoint were spokesmen for Iran’s foreign ministry, Russia’s foreign ministry and Hezbollah. When the only people condemning the air campaign are America’s worst enemies, it’s not hard for the reader to see who they’re supposed to side with.
The fact is, the Houthis have withstood a decade of strikes by Saudi Arabia and the United States with no signs of faltering. Indeed, as Jennifer Kavanagh (Responsible Statecraft, 3/17/25) has pointed out, the Houthis’ “willingness to take on American attacks lend them credibility and win them popular support.” In a story whose subheadline mentions a claim that children were killed, the Times is irresponsible to present the only solution as more bombs, more aggression, more killing.
‘Iranian-backed’

The US has long been implicated in a string of atrocities in Yemen (Guardian, 8/19/18).
In each of their five stories on the strikes, the New York Times referred to the “Iran-backed” or “Iranian-backed” Houthis, playing into the false notion that the Houthis are little more than Iran’s lapdogs in the Arabian Peninsula. Even the Washington Post, to their credit, was able to find a distinction between an ally of Iran and a proxy (e.g. 3/15/25, 3/27/25).
The Times also had a case of amnesia over the circumstances of Yemen’s protracted civil war and famine. Two stories (3/15/25, 3/27/25) mentioned the Houthi victory over a “Saudi-led coalition,” culminating in a 2022 truce, still holding tenuously. What was left unsaid was the US role in that conflict.
During the Yemeni civil war, the United States provided Saudi Arabia with plenty of firepower and logistical support to prosecute their brutal military intervention. The Department of Defense gave over $50 billion in military aid to Saudi Arabia and the UAE between 2015 and 2021 (Responsible Statecraft, 3/28/23). Despite campaign promises to the contrary, the Saudi blockade and accompanying humanitarian crisis were intact over two years into President Biden’s term of office.
Infamous airstrikes using US-made weapons include a wedding bombing that killed 21, including 11 children, a school bus bombing that killed 40 elementary school-aged boys along with 11 adults, and a market bombing that killed 107 people, including 25 children, just to name a few (CNN, 9/18; Guardian, 8/19/18; Human Rights Watch, 4/7/16). The continuous provision of weapons, training and logistical support amounted to complicity in war crimes (Human Rights Watch, 4/7/22).
Deadly effects

The Yemen where tens of thousands of children died as a result of a US-backed blockade (New York Times, 11/21/18) seems like a different country than the one discussed in a bumbling group chat.
The civil war in Yemen, which began in late 2014, has killed hundreds of thousands. From 2015–22, Saudi-led, US-backed airstrikes killed nearly 9,000 civilians, including over 1,400 children.
More deadly than the bombs and other weapons of war are the indirect effects of the war, namely disease and famine. A 2021 UN report estimated that 60% of the 377,000 deaths in the Yemeni civil war came from indirect causes (France24, 11/23/21). By 2018, Save the Children reported that by a “conservative estimate,” 85,000 children had died from hunger (New York Times, 11/21/18). Today, nearly 40% of the Yemeni population are undernourished, and nearly half of children under five are malnourished.
This ongoing famine started during the war, and has been enforced by a Saudi blockade. While the 2022 truce allowed a trickle of international shipping to Houthi-controlled Yemen, cuts in humanitarian aid have kept Yemenis in precarity (The Nation, 7/27/23).
Since the Yemeni civil war began, not enough attention has been paid to the compounding crises in the region: the civil war itself, the accompanying famine and the Biden administration’s own ill-advised bombing campaign. As juicy as one more Trump administration blunder might be, newsrooms should not lose track of the fact that this military offensive, just beginning, is already stained by violations of international law.
This post was originally published on FAIR.