
Along with its upcoming fundraise, Simple Planet is about to submit dossiers in South Korea and Singapore for regulatory approval – a feat its CEO says will make cultivated meat resurgent.
Despite continued declines in funding and escalating political challenges, regulatory progress shows that cultivated meat can weather the storm, according to the CEO of one major industry player.
Funding for cultivated meat startups shrunk by 75% in 2023, and another 40% last year, just as politicians in Italy, Florida, Alabama, and now Mississippi have banned the sale and production of these proteins. The industry, meanwhile, continues to face major headwinds due to high R&D costs, scaling difficulties, and the macroeconomic landscape.
“However, as more bio-food tech companies gradually receive regulatory approvals from various countries, we remain optimistic that the cultivated meat sector will continue to expand, leading to a resurgence in investment and funding,” says Dominic Jeong.
He is the co-founder and CEO of Simple Planet, a South Korean food tech startup that is taking a unique approach to cultivated meat. It produces cell-cultured ingredients like proteins (specifically, amino acids) in powder and paste formats, and omega-3 fatty acids in the form of an oil and a paste.
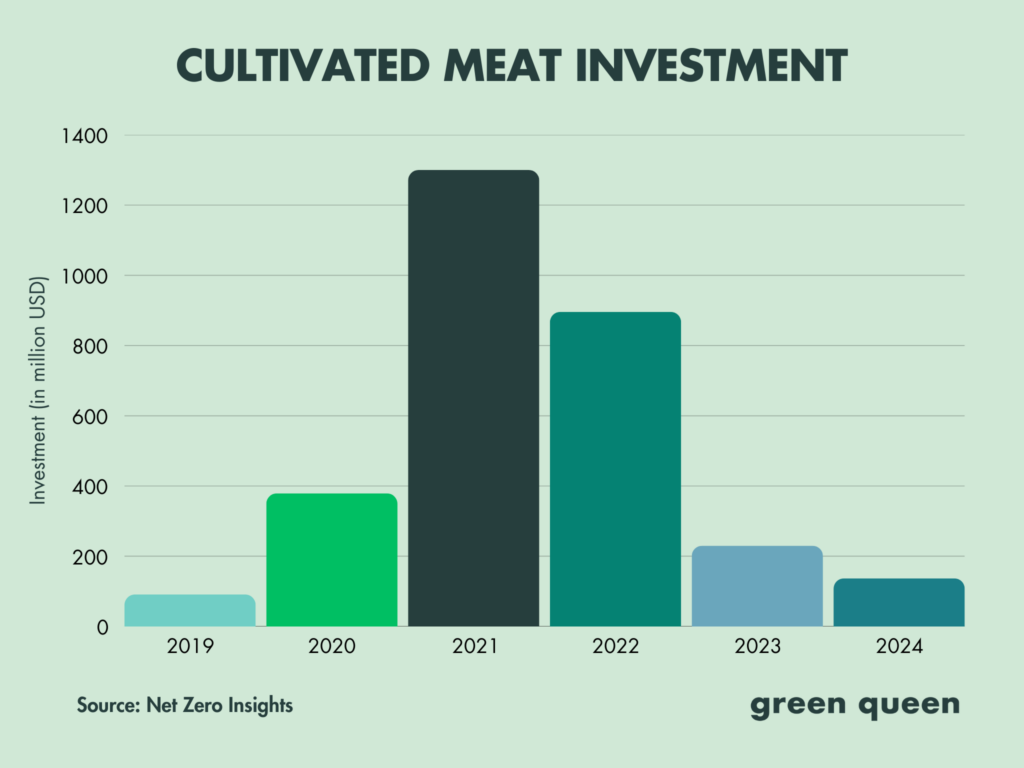
The firm – which is prioritising beef, chicken, and fish from its suite of 13 cell lines – is preparing regulatory dossiers for food safety authorities in South Korea and Singapore, aiming to file them within the first half of this year. It means its products could come to market in 2026, given the timeline of approvals in each country.
“We are initially working on a muscle-derived cell line. This cell line will be submitted for regulatory approval upon completion of the necessary application data,” Jeong tells Green Queen.
Simple Planet also has an eye on Thailand and Indonesia, and is amplifying its presence in the Middle East and North America. These efforts will be helped by its upcoming bridge loan worth $10M, Jeong notes.
“It’s a complex time for cell-based food globally, particularly in funding and regulation,” Jeong says. “With investors becoming more cautious, having a clear path to market and a scalable business model is more important than ever. At Simple Planet, we’ve stayed focused on efficiency, partnerships, and long-term viability.”
The company has already raised $8M from investors, in addition to an $8M government grant it received as part of a food security project last year. The new funding, the CEO says, will primarily be used to drive commercialisation, establish an industrial production facility, and expand Simple Planet’s business operations.
Simple Planet’s multi-pronged path to market
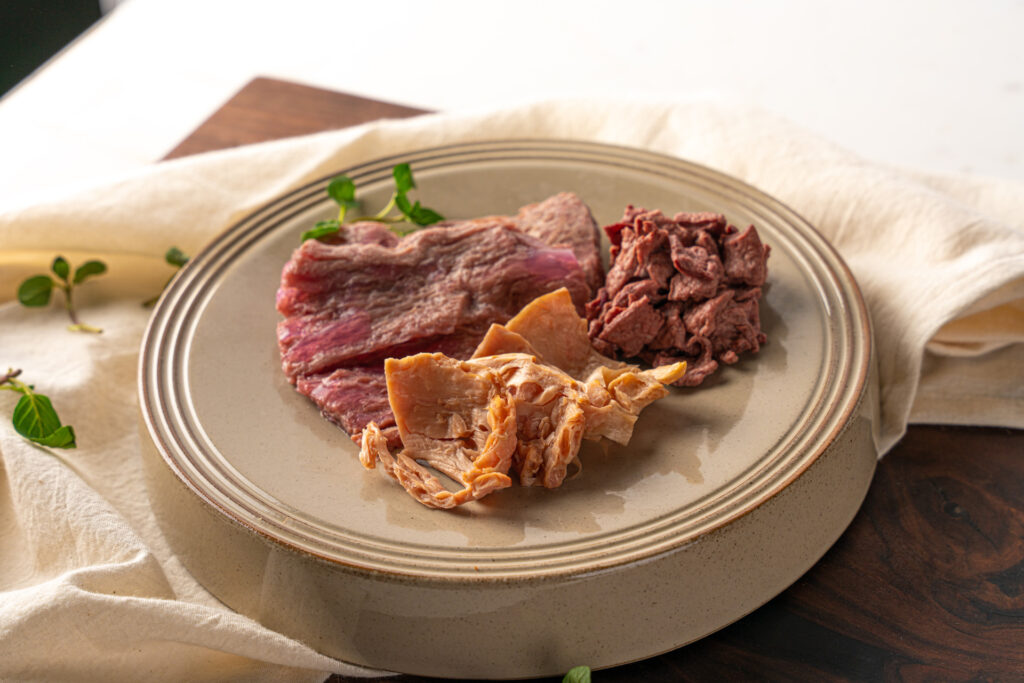

Simple Planet is producing a lyophilised cell powder with 16 times more protein than whey. “The powder has the potential to effectively substitute the whey protein currently used in Formula 75 (F-75) and Formula 100 (F-100), which are therapeutic milk formulations designed for the treatment of severe malnutrition,” explains Jeong.
“We are actively engaged in efforts to replace whey protein in these products to provide a reliable and effective source of protein nutrition.”
In addition to these ingredients, it has unveiled Balboa Kitchen, a healthy snacking brand featuring ready-to-eat granola, functional snacks, and “other clean-label products” made from the cell-based ingredients.
“We’re planning to enter global markets this year, starting with Southeast Asia and Japan, where demand for Korean-made healthy food continues to grow,” reveals Jeong.
Meanwhile, Simple Planet’s patented serum-free culture medium replaces fetal bovine serum with probiotic-derived metabolites, slashing costs by over 99.8% and addressing key ethical concerns. “Our serum-free culture media is aimed at research labs and biotech startups, particularly those working on cell-based food. We’re leveraging our network to support innovation across the industry,” he says.
Since its innovations are ingredients rather than fully formed products, a direct comparison with the cost of conventional meat is not an appropriate measure, Jeong argues. “However, the initial cost per kilogram is comparable to that of conventional meat, while the protein content per unit weight is significantly higher. As production scales up to industrial levels, the cost is expected to decrease significantly,” he explains.
“Our scale of production is using 1,000-litre bioreactors, and the capacity goal of ingredient production is a maximum of 3.2 tonnes per month,” he adds. “Our facility is currently in the process of obtaining GMP [Good Manufacturing Practice] certification, which will ensure that our production is conducted in a highly controlled, contaminant-free environment.”
Simple Planet is targeting CPG players with the cultivated protein and fat. “We aim to produce at scale and collaborate with food conglomerates to enhance the nutrition of their products. These ingredients are highly versatile and can be applied to snacks, beverages, ready meals, and more,” says Jeong.
“We’ve already completed successful proof-of-concepts with major Korean players like Nongshim and CJ, developing more nutritious versions of products like instant noodles and gyoza.”
Several projects underway to advance cultivated meat

The purpose of the bridge funding is fourfold. Simple Planet will aim to set up a large-scale production plant, establish strategic partnerships for product integration with food and beverage companies, expand its presence in global markets while pursuing regulatory approval, and hire top biotech, food science, and commercialisation experts to help execute these goals.
In the meantime, it has embarked on several projects to advance its path to market. One of these is a proof-of-concept collaboration with a “global food conglomerate” to explore how its ingredients can enhance the taste and nutrition of its products across the food, beverage, supplement and wellness categories.
“We are also exploring ways to support Indonesia’s national priority programme for free nutritious meals, working with local partners to contribute to sustainable and accessible nutrition solutions,” says Jeong.
In February, Simple Planet announced it was collaborating with Chulalongkorn University’s Halal Research Center in Thailand to integrate Halal standards into its manufacturing practices. After the startup initiated discussions and shared data on its technology, the Korean Muslim Federation issued a fatwa confirming that cultivated meat can be consumed by Muslims if it meets certain criteria.
In addition, the company is working with the Indonesian National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN) and Thailand’s National Food Institute to advance the development of cell-cultured ingredients. And the startup has signed an MoU to partner with the newly announced cultivated meat research centre in Uiseong County.
“For Simple Planet, government approval and halal certification are top priorities,” says Jeong. “We work closely with halal authorities and food regulators to ensure our serum-free, halal-compliant cell culture medium meets industry standards.”
Cultivated meat needs ‘stronger government support’

Simple Planet has been engaging with regulators across key markets, including the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (which established a novel food framework in 2024 and is expected to greenlight an application from local startup CellMeat soon). Further, it’s working with the Singapore Food Agency and the National Agency of Drug and Food Control (BPOM) in Indonesia.
“In Indonesia, Thailand, South Korea, and Singapore, there is increasing interest in alternative proteins as part of national food security and sustainability initiatives,” says Jeong. “Singapore has led the way with a regulatory framework, while other countries are actively developing policies on food safety and halal compliance.”
He calls for “stronger government support” in regulation, research, and halal certification, which is crucial to unlocking the full potential of cultivated meat in mainstream markets.
So far, cultivated meat has been cleared to be sold in Singapore (from two startups), the US (four), Israel, the UK, Hong Kong, and (preliminarily) Australia and New Zealand (one each). Despite all the turmoil in the sector, three approval decisions have come this year. Regulators in the EU, Switzerland, Thailand and South Korea are assessing applications too.
“Regulatory progress varies widely – countries like Singapore and the US are moving forward, while others are still developing frameworks. This creates uncertainty, but also opportunities to help shape the conversation,” says Jeong.
“Europe remains cautious about the commercialisation of cell-based food, although some products have entered the market as pet food. This might be an early sign that Europe may gradually open up to cultivated meat in the future,” he adds. Even in Singapore and Israel, challenges remain in terms of standardisation, market access, and regulatory consistency.
But he indicates that the wave of approvals over the last 18 months is a sign of good things to come after a period of turbulence: “These hurdles appear to be part of the natural progression of introducing a new technology to consumers, and we believe they will be resolved in the near future.”
The post Regulatory Approvals for Cultivated Meat Will Bring Investors Back, Predicts Simple Planet CEO appeared first on Green Queen.
This post was originally published on Green Queen.