
Alternative protein think tank the Good Food Institute has released its annual State of the Industry series of reports, covering plant-based, cultivated and fermentation-derived proteins. Here are the key takeaways.
Political resistance and a drop in funding and sales were offset by a hike in manufacturing facilities, diverse partnerships, and regulatory approvals in the alternative protein world last year, according to the 2023 State of the Industry reports by the Good Food Institute (GFI).
Comprising plant-based, cultivated and fermented proteins, the reports outline the progress, challenges, and future of the industry. Globally, retail sales for plant-based meat, seafood and dairy saw a slight increase, from $28B in 2022 to $29B in 2023. But the road towards taste and price parity, improved accessibility, better nutrition, and significant market penetration remains lengthy, with GFI comparing this to Hofstadter’s Law.
Coined by scientist Douglas Hofstadter, it reads: “It always takes longer than you expect, even when you take into account Hofstadter’s Law.” It’s meant to describe the difficulty of estimating how much time it will take to complete complex tasks. “As Hofstadter’s Law and similar adages dictate, this will take time,” says GFI business analyst Daniel Gartner, drawing parallels with alternative protein’s progress. “However, keep our eyes on the goal post and the vision all of us in this industry are working towards – a brighter food future for people and the planet.”
Here are the key highlights from the 2023 State of the Industry reports:
Plant-based milk on the up, but meat and seafood suffer
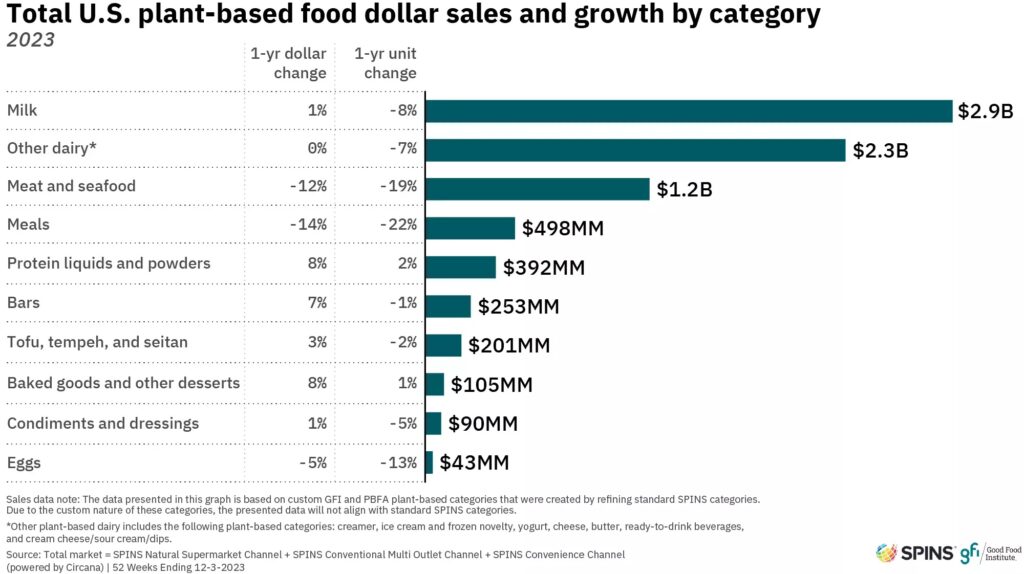
The plant-based food market in the US saw $8.1B in dollar sales in 2023, down by 2% from the year before. This meant the industry represented 1.1% of the overall food sector’s sales. But looking at longer-term trends, global sales for plant-based meat have nearly tripled from $2.2B in 2014 to $6.4B in 2023.
For plant-based meat and seafood, the decline was larger, representing the macroeconomic challenges faced by the category. Here, US retail dollar sales fell by 12% to $1.2B. Sales for conventional meat and seafood, in comparison, flatlined – but the average price per unit was only up by 3%, compared to 9% for plant-based analogues, which now make up 0.9% of the overall meat market. Burger patties are the most popular, followed by nuggets, tenders and wings, and grounds.
Things were slightly more positive on the plant-based milk side of things, where sales grew slightly by 1% to reach $2.9B and take up 14.5% of the overall milk sector in the US. Almond is still king, capturing 56% of the market, with oat continuing its ascendancy (24%).
When it comes to consumer adoption, 62% of households bought vegan products, with meat and seafood reaching 15% of homes, and milk 44%. Encouragingly, the repeat purchase rates were high at 81% for the entire category, 79% for milk, and 62% for meat and seafood analogues.
Beef is closest to price parity, eggs farthest
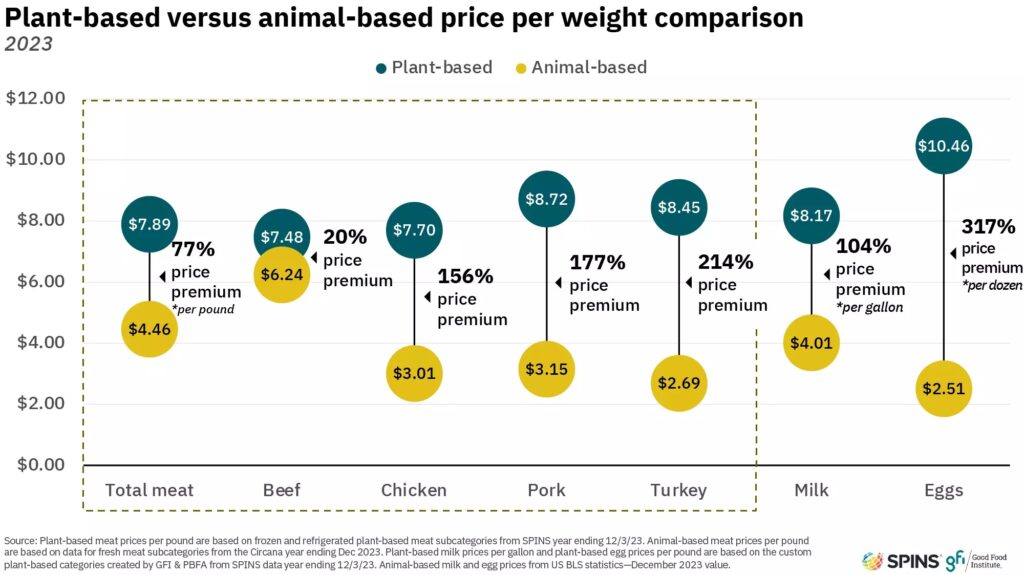
GFI notes that the price gap between plant-based and conventional proteins is still a significant purchase barrier, outlining that grocery costs were the key economic concern for consumers last year. And 2023 was challenging for the vegan sector in this aspect – while plant-based foods saw a lower price growth than the overall food sector and some conventional categories in 2022, the former’s markups were higher in 2023.
From 2021 to 2023, plant-based meat and seafood’s average price per unit rose by 17%, compared to 16% for their conventional counterparts. Last year, the average price premium for plant-based meat and seafood was 77%. That said, beef is currently the vegan analogue that’s closest to price parity, with plant-based versions costing $7.48 per pound, versus $6.24 for the same amount of animal-derived beef – a 20% difference.
The gap is much larger in other categories. For milk, this comes to 104%, while eggs have the highest price premium at 317%. Even other meat categories need to bridge this gap, with vegan chicken costing 156% more, pork 177% and turkey 214%.
Alternative protein investments underestimated
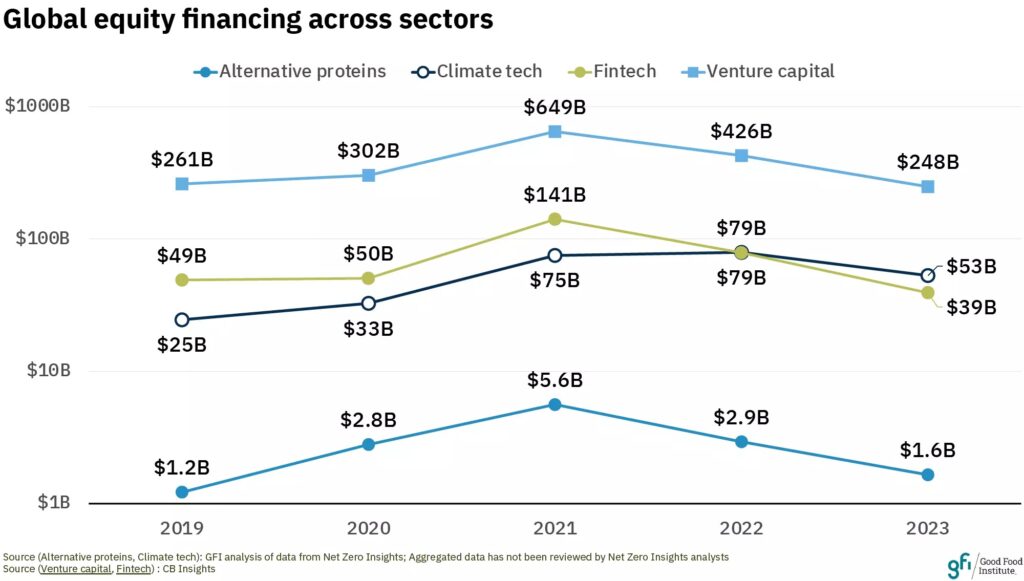
A host of reports over the last few months have showcased the dire situation of VC funding in the food tech sector. Globally, agrifood tech companies brought in 49% less capital in 2023 than the year before, according to one report.
The data cited by GFI signals a 42% in overall VC investment across all sectors, with a 40% drop in climate tech, 51% fall in fintech, and 61% decline in food tech financing. For alternative protein companies too, funding dipped by 44% from $2.9B in 2022 to $1.6B in 2023. This was dominated by plant-based startups ($907M), followed by fermentation ($515M) and cultivated meat ($226M) companies. Collectively, these sectors have secured $15.7B in all-time investment.
“The sales and investment slowdowns in 2023 weren’t unique to the alternative protein industry, but as a relatively nascent sector relying on private investments to navigate early-stage operations and strong sales performance to secure favourable placements on retail shelves, they played outsized roles in the sector’s 2023 performance,” writes Gartner.
But GFI suggests that these totals are likely understated, with some funding rounds not publicly disclosed. While that is the case for certain deals in general anyway, this year may have had a higher frequency due to a large number of simple agreements for future equity (SAFE) and bridge rounds, and based on its conversations with market participants. Some of these rounds may be reported this year.
Despite that, investments in Europe actually increased for the second consecutive year, reaching $584M (up by 74%), a record total for the region. It was the first time European investments comprised over half of all invested capital in the plant-based industry.
Legislative wins and challenges for alternative protein

Despite the private investment dip, public financing for these sectors matched the record levels of 2022. Canada announced C$150M for Protein Industries Canada, Germany set aside €38M in its federal budget for a sustainable protein transition, the US committed $40M in fermentation funding over four years, and the UK injected £15.4M in multiple cultivated meat projects.
However, GFI noted that total public investment in 2023 only met a tiny fraction of the estimated $10.1B in annual support needed to realise the full potential of alternative proteins.
It has been a rollercoaster year in terms of regulation for cultivated meat and precision fermentation. The US joined Singapore as the second country to allow the sale of cultivated meat. Israeli precision fermentation company Remilk received a ‘no further questions’ letter from the FDA to cement its Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), while The Every Co obtained its third such certification in late 2023. Imagindairy and TurtleTree, meanwhile, earned self-affirmed GRAS status (with a ‘no further questions’ letter coming in January this year for the former).
Since then, Israel has also joined the list of countries that have approved cultivated meat, while Singapore issued its second certification earlier this month. Precision fermentation companies like New Culture, The Protein Brewery, Vivici and Oobli have achieved some form of GRAS status in the US too.
But there have been challenges as well, with Florida on the verge of banning cultivated meat, and Alabama, Arizona, Wisconsin, Texas, Nebraska and Tennessee all proposing similar bills. Across the Atlantic, Italy became the first country to ban cultivated meat, while a group of countries asked the EU to rethink its already-stringent novel foods regulations. France and Romania are also considering a ban on these proteins.
More facilities, more jobs

In spite of the tough funding environment and legislative challenges, there has been an increase in both the number of companies and production facilities for alternative proteins. There are now 174 businesses working on cultivated meat across the supply chain (up from 166 in 2022), and 158 on fermentation-based proteins (versus 136 in 2022).
Meanwhile, 2023 saw 10 new cultivated meat facilities open, while seven fermentation plants began operating too. And several more sites were announced across the alt-protein spectrum too. According to the ClimateWorks Foundation and the Global Methane Hub, this trend means the industry could support up to 83 million jobs internationally by 2050.
“However, the alternative protein sector is not yet positioned to capture those levels of economic impact,” notes Gertner. “The plant-based, fermentation, and cultivated industries exist in distinct stages of industry development, but the average quality and availability of alternative protein products do not yet meet consumer expectations. To approach significant market penetration levels, alternative protein companies need to continue to improve product cost, taste and volumes.”
He implores governments, companies and investors to dedicate more research and investment towards alternative proteins, if they’re “serious about improving food security, reducing emissions, and achieving climate goals”. “By scaling, reducing costs, and improving taste and texture, alternative proteins – alongside other advances and innovations –can continue to shape the future of food and agriculture,” he said.
The post Price Parity, Job Creation & Investment: Highlights from GFI’s Alt-Protein State of the Industry Reports 2024 appeared first on Green Queen.
This post was originally published on Green Queen.