Donald Trump is back in office. Tech mogul Elon Musk, now a senior adviser to the president, is helming a government advisory body with an acronym derived from a memecoin: DOGE (Department of Government Efficiency). That organization is sinking its teeth into the federal government, and drawing blood.
Tens of thousands, maybe hundreds of thousands, of federal employees are being laid off this year. Over a dozen agencies have been affected. Executive power is being wielded so wildly that a federal judge has lamented “what appears to be the unchecked authority of an unelected individual and an entity that was not created by Congress and over which it has no oversight.”
The Fourth Estate is tasked with serving as a check on abuses of power. But US media were not designed for this.
Though critical in much of their reporting, corporate outlets have at the same time substantially legitimized the project of DOGE. For one, longstanding fearmongering about government spending in the news sections of corporate outlets has elevated precisely the right-wing vision of government animating DOGE.
Even more worryingly, however, criticism of DOGE by major editorial boards has been weak, and in some cases has been overshadowed by these boards’ support for the ideas behind DOGE, or even for DOGE itself.
Government spending ‘skyrocketed’
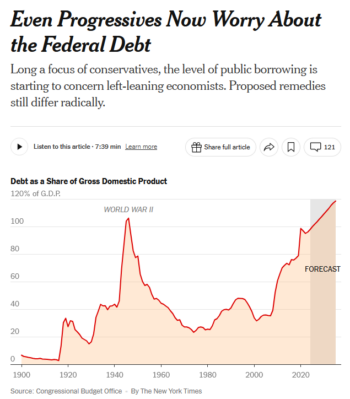
The New York Times (1/30/25) claims “even progressives now worry about the federal debt”—though an extensive recent analysis (PERI, 4/20) of the impact of debt by progressive economists found that “the relationship between government debt and economic growth is essentially zero.”
Corporate media’s ever-present fearmongering about spending is well-illustrated by the New York Times, which, within a week and a half of Trump’s inauguration, had already run the headline: “Even Progressives Now Worry About the Federal Debt” (1/30/25). The next day, the paper ran a separate article (1/31/25) by Michael Shear, which stated:
The amount of money the government spends has skyrocketed under Democratic and Republican presidents. Total federal spending in 2015 was $4.89 trillion, according to federal data. In 2024, it was $6.75 trillion. Even when accounting for the growth of the overall economy, spending as a percentage of gross domestic product was higher in 2024 than it was eight years earlier.
The paragraph at least avoided the classic tactic of throwing out raw numbers without giving any sort of metric, like GDP, to measure them against. But it nonetheless gave far from the full picture, not even offering numbers for spending as a percentage of GDP, which showed a minor increase of 3 percentage points over this period, to 23%—the same percentage that was spent in 2011.
Even more useful to include than this data, however, would have been international data showing how much the US spends in comparison to other rich countries. As it turns out, the answer is: quite little. And the US taxes even less.
Readers might also be interested to learn that tax cuts, not spending increases, have been primarily responsible for increases in the US’s debt-to-GDP ratio in recent decades, according to an analysis by the Center for American Progress (3/27/23). The group emphasized: “Without the Bush and Trump tax cuts, debt as a percentage of the economy would be declining permanently.” Given that reality, CAP concluded:
If Congress wants to decrease deficits, it should look first toward reversing tax cuts that largely benefited the wealthy, which were responsible for the United States’ current fiscal outlook.
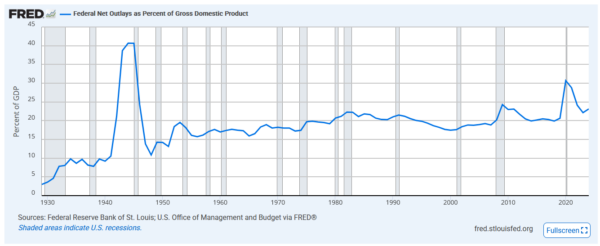
Federal outlays as a percentage of GDP have been nearly constant for the past 75 years (FRED).
‘The big areas of the budget’
The New York Times‘ Michael Shear (1/31/25) wrote that Trump was attempting “to somehow reverse the seemingly inexorable growth of the federal government, an issue that resonates with some Democrats as well as most Republicans.”
If corporate media like the New York Times were serious about informing readers about the causes of and answers to high government debt, they would, like CAP, debunk right-wing deficit hawk propaganda, rather than reinforce it.
Instead, the Times‘ Shear (1/31/25) decided to provide his readers with extensive quotation from Maya MacGuineas, an extreme deficit hawk who got an early boost in her career “from the patronage of billionaire investment banker and arch-austerian Pete Peterson,” as the New Republic (3/4/21) recounted in a 2021 piece. Shear merely described her as “the president of the bipartisan Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget.”
MacGuineas is the only expert Shear cites in the piece, and the article closes with her warning that Musk’s cuts “would not be enough to confront the nation’s burgeoning debt from spending too much over many decades.” “To make a real impact on the debt,” MacGuineas said:
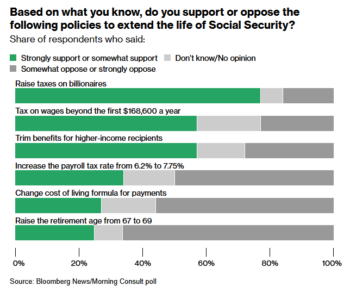
We are going to have to look at the big areas of the budget for savings—Social Security, healthcare and revenues—the very same areas both political parties are tripping over themselves not to address.
The decision to include only an austerity advocate, and to allow her proclamation about the need for cuts to Social Security to end the piece, inevitably grants legitimacy to her claims. These claims are at the very least meant to be taken seriously, even more so since they come from a supposedly independent expert rather than a politician or government official. The decision to include no left-wing expert has a similar effect in reverse.
Meanwhile, in the paper’s piece (1/30/25) from the previous day about “progressive worry,” reporter Lydia DePillis managed to bury the key point in the 21st paragraph:
But mostly, Democrats say, the government simply needs more revenue to support the increasing number of people who are becoming eligible for retirement benefits.
Debt-scolding reporting
The Washington Post (10/8/24) sounds the alarm over the United States having a debt-to-GDP ratio similar to that of Britain, France and Canada—and much lower than Japan’s.
The Times is hardly the only outlet to legitimize alarmism about government spending. In a debt-scolding piece of reporting from last fall, the Washington Post (10/8/24) hammered on the point that runaway spending should be a major concern.
The choice of headline, “US Deficit Hits $1.8 Trillion as Interest Costs Rise,” immediately linked debt concerns to spending, not taxes. The first paragraph described the $1.8 trillion figure as “an enormous sum”—probably equally applicable to any sum over a billion dollars in the average American’s mind—while the fourth paragraph warned:
The nation’s debt compared with the size of the overall economy, a key metric of fiscal stability, is projected to exceed its all-time high of 106% by 2027.
Once again, international comparison would have been helpful here. It could be noted that the US, in fact, has a rather typical amount of debt compared to many other rich countries these days, with Britain, Canada, Spain, France and Italy all posting similar debt-to-GDP numbers. Greece, meanwhile, has a debt-to-GDP ratio close to 170%, while Japan boasts a ratio of around 250%. As Mark Copelovitch, a professor of political science and public affairs at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, has noted:
If these countries can sustain debt levels 50–150% higher than our current levels, then the question of whether we can do so has already been answered. Indeed, it does not even need to be asked.
The Post, evidently, had no interest in providing such context. No international figures were cited. Instead, the next lines were a quote from a conservative economist:
A [nearly] $2 trillion deficit is bad news during a recession and war, but completely unprecedented during peace and prosperity…. The danger is the deficit will only get bigger over the next decade due to retiring baby boomers and interest on the debt.
Notice once more the linking of the increase in debt to spending rather than tax cuts.
The ‘soaring’ debt that wasn’t

The federal debt the Wall Street Journal (9/16/24) claimed was “soaring” was a smaller percentage of GDP in 2024 than in 2020.
The piece continued on to cite deficit hawk MacGuineas—described as the president of “a top Washington fiscal watchdog”—denouncing the “patchwork of targeted fiscal bribes” being offered to voters by the presidential candidates. And it ended with a quote from “president of the right-leaning American Action Forum and a former CBO director” Doug Holtz-Eakin, reminding us that debt servicing costs will have to be paid and will crowd out other spending priorities.
Unmentioned by the Post is that Holtz-Eakin held high posts in the George W. Bush administration and the John McCain presidential campaign. He also oversaw the creation of an infamous bogus cost estimate for the Green New Deal. Yet the Post portrays him as just an expert who leans a bit to the right.
Though the Post consulted three right-wing sources, they failed to include a single left-leaning independent expert. It’s not hard to understand how that fails readers, or how it legitimizes a certain set of priorities, while suggesting other views lack credibility.
The Wall Street Journal, for its part, has been more than happy to join the general fretting in corporate media about government spending. Back in the fall, for instance, a piece in its news section (9/16/24) complained that the presidential race was not focusing sufficiently on the issue of rising government debt, and flagged Social Security and Medicare as “the biggest drivers of rising spending.” The headline read: “Federal Debt Is Soaring. Here’s Why Trump and Harris Aren’t Talking About It.”
The problem with that headline? In the fall of 2024, federal debt was decidedly not soaring. This holds whether you look at federal debt in nominal dollar terms or as a percentage of GDP. Federal debt had “soared” briefly in 2020, when the Covid recession hit and the government rapidly expanded its spending to deal with the downturn. But for most of 2024, the quarterly percentage increase in the federal debt in dollar terms was actually below the historical average going back to 1970. And the debt-to-GDP ratio was at roughly the same spot as it had been three-and-a-half years earlier, at the start of Biden’s presidency.
‘Shutting off the lights’

For the Wall Street Journal (2/10/25), refusing to cut Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid “is like saying you want to go on a diet except for the beer, chips and ice cream sundaes.”
Even more concerning than corporate media’s penchant for running articles in the news section fearmongering about government spending, though, is what has been going on in corporate outlets’ opinion sections, specifically with the output of their editorial boards. Here, the legitimization of DOGE has reached its highest heights.
Unsurprisingly, the unabashedly right-wing Wall Street Journal editorial board has been the prime offender. Most recently, it published an editorial (3/14/25) with the headline “Don’t Cry for the Education Department,” applauding the unconstitutional DOGE-led attack on the Education Department, which the Journal chastened for “harassing schools, states and districts with progressive diktats on everything from transgender bathroom use to Covid-19 mask rules.”
The final paragraph began: “The closer Mr. Trump can get to shutting off the lights at the Education Department, the better.”
This was just one of numerous Journal editorials in recent weeks cheering on the DOGE project. A sampling of other editorials:
- “Hurricane Musk and the USAID Panic” (2/4/25) argued that Musk should be contained, but that he is “also hitting targets that have long deserved scrutiny and reform, which helps explain the wailing over the US Agency for International Development.”
- “The Federal Spending Boom Rolls On” (2/10/25) declared that “DOGE is a good idea,” and claimed that it had not gone far enough: “But for all of Mr. Musk’s frenetic tweeting, and the Beltway cries of Apocalypse Now, so far DOGE is only nibbling at the edges of Washington’s spending problem.”
- “Judge Wants DOGE Facts, Not Fears” (2/19/25) ended, “Democrats hunting for a constitutional crisis might want to show evidence before they cry ‘dictator.’”
In short, then, the Journal editorial board not only approves of a rogue pseudo-agency operating with no transparency or oversight, but has become a crusader in defense of DOGE’s attacks on constitutional checks and balances—which grant Congress, not a right-wing ideologue from the PayPal Mafia, the power of the purse.
Of course, you can expect little else from the Journal than salivation over cuts to federal spending—it has long been the lapdog of right-wing billionaire Rupert Murdoch. But it is jarring to witness exactly how rabid the Journal editorial board can be.
Not ‘audacious’ enough
The Washington Post says it’s “true that the $36 trillion national debt is unsustainable and there’s plenty of bloat in government.”
For its part, the Washington Post editorial board, while describing DOGE as a “circus” (2/24/25), has substantially legitimized DOGE’s mission.
An editorial (2/7/25) from early February is case in point. Headlined “Trump Needs to Erect Guardrails for DOGE,” the piece offered five ways for Trump to “be clear about who is boss,” effectively endorsing the mission of slashing government spending while expressing concern over some of Musk’s tactics.
The first four proposed guardrails in the piece, which include “Vet Musk’s operatives” and “Limit Musk’s access to sensitive files,” are all reasonable, but the fifth proposal reveals the board’s substantive concerns about the spending cuts being executed by DOGE. These concerns are not about whether cuts should be made—it is taken for granted that government spending should be reduced. Rather, they have to do with which spending is cut, aligning with the concerns raised by the Wall Street Journal about DOGE not going far enough.
This proposal, labeled “Focus on the biggest drivers of the national debt,” read:
To have any chance of achieving Musk’s audacious goal of $2 trillion in cuts, Trump will need to work with elected representatives in Congress to reform entitlement programs such as Social Security and Medicare before they become insolvent. Other sensitive areas of the balance sheet, including the Pentagon budget and veterans’ benefits, cannot stay off the table forever.
For the Post, then, the focus on programs such as USAID is simply too limited. We must put Social Security, Medicare and veterans’ benefits on the table!
‘Embrace the same thinking’
The “DOGE ethos,” according to the Washington Post (3/3/25), means making “governments leaner and more efficient.”
The Washington Post’s preference for substantial cuts to federal government is further illustrated by an editorial (3/3/25) published in early March, following Jeff Bezos’s rebranding of the Post as Wall Street Journal–lite.
The editorial, titled “The DOGE Ethos Comes to State Governments,” showered praise on state governments that are capitalizing on DOGE branding while pursuing a more “thoughtful” approach to reducing government spending.
The piece favorably cited Washington state Democratic Gov. Bob Ferguson’s insistence that “I’m not here to defend government…. I’m here to reform it.” The board elaborated:
Democrats in DC ought to embrace the same thinking. It’s foolish to defend a status quo that most voters think doesn’t work well. By fighting Trump and Musk tooth and nail, at the expense of presenting an alternative vision, the opposition risks appearing overly keen to protect hidebound institutions even as the world changes rapidly.
The Post’s take on DOGE? Let’s not center its blatant illegality. Let’s instead focus on what we can learn from it. After all, with a few minor tweaks, it’s exactly what we as a country need.
‘A great American success story’

New York Times says of Elon Musk, “he’s right: The federal government is often wasteful and inefficient.” But he’s going about it the wrong way.
The appallingly low bar set by the competition leaves the New York Times to assume the role of the major national newspaper that will seriously attack DOGE. It takes to this role…poorly.
The Times editorial board’s pushback against DOGE has been embarrassingly feeble. Its most direct assessment of DOGE thus far (3/8/25), for instance, began with an uncomfortably obsequious description of Musk:
Elon Musk’s life is a great American success story. Time and again, he has anticipated where the world was headed, helping to create not just new products but new industries.
The board quickly conceded a major point to Musk:
Mr. Musk claims that the government is a business in need of disruption and that his goal is to eliminate waste and improve efficiency. And he’s right: The federal government is often wasteful and inefficient.
The editorial went on to make a number of criticisms of DOGE, but its critique was undermined by this odd willingness to bend over backwards to appease Musk and his supporters.
Meanwhile, though sharply critical of DOGE’s disregard for the Constitution, the editorial made no attempt at presenting a counter-vision of government. It lamented cuts to a hodgepodge of specific government programs, but it had nothing to say in defense of current levels of government spending, let alone in favor of even higher levels of spending. One would hardly know that many wealthy countries have significantly higher levels of government spending and happier populations—in fact, at least 16 OECD countries register both higher spending and higher happiness than the US.
A gaping hole
This, then, is the state of American corporate media at the start of the Trump presidency. Across arguably the three most important national newspapers—the New York Times, the Washington Post and the Wall Street Journal—there is broad agreement that government spending is out of control and that something, perhaps something drastic, needs to be done about it.
Even at the leftmost of these organizations, the New York Times, the editorial board appears incapable of mounting a case for social democratic levels of government spending in the face of extreme attacks on spending by the Trump administration. The Times, instead, finds itself caught between bowing before the titans of American capitalism and confronting their disregard for the US Constitution.
The Washington Post has been able to adopt a somewhat less tortured position, occupying the center/center-right in a way reminiscent of 1990s Democrats, supporting cuts to government, but in a “thoughtful” way.
The Wall Street Journal, meanwhile, is having the time of its life. Finding itself once again in an era when greed and meanness animate the daily actions of government, it must feel freer than it has in years to bare its teeth at the true enemies of the American republic: teachers’ unions and recipients of government aid.
News consumers have no major paper espousing a truly progressive perspective. On the topic of government spending, at least, the window of acceptable thought appears to span from the center to the far right. There is no direct marketing reason for this—there’s a sizeable audience in the US that would welcome a progressive outlet, the same way there’s a sizeable audience for right-wing outlets like the Wall Street Journal or Fox News.
Who doesn’t want such an outlet to appear? Ultra-wealthy right-wing Americans of the sort that own and sponsor much of the media landscape. If wealthy people aren’t willing to finance a progressive media outlet that can compete with major papers, it seems that such an outlet simply won’t exist. Crowdfunding could help progressive media overcome this issue, but the playing field is not level.
As it stands, a major progressive outlet that can compete with the existing dominant players does not exist, and does not seem to be coming anytime soon. The gaping hole left as a result is becoming only more apparent as we speed into Trump administration 2.0.
This post was originally published on FAIR.

 A clip from Minister Wilkinson’s letter in response to oil and gas CEOs.
A clip from Minister Wilkinson’s letter in response to oil and gas CEOs.












































 On top of that, Donald Trump and his administration have made a point to dismiss Canada’s independence by referring to Canada as the “51st state”.
On top of that, Donald Trump and his administration have made a point to dismiss Canada’s independence by referring to Canada as the “51st state”.