Waging Nonviolence (3/19/25)
“Resistance is alive and well in the United States.”
So declared the headline of a March 19 article on the nonprofit news site Waging Nonviolence. Authors Erica Chenoweth, Jeremy Pressman and Soha Hammam, political scientists at Harvard’s Crowd Counting Consortium, outlined how—despite a common belief that grassroots public resistance against the depredations of the Trump Administration is lacking or lukewarm—protests are actually rising dramatically.
These demonstrations, the piece said, “may not look like the mass marches of 2017, but research shows they are far more numerous and frequent—while also shifting to more powerful forms of resistance.”
They note that while
the reconfigured Peoples’ March of 2025—held on January 18—saw lower turnout than the 2017 Women’s March, that date also saw the most protests in a single day for over a year. And since January 22, we’ve seen more than twice as many street protests than took place during the same period eight years ago.
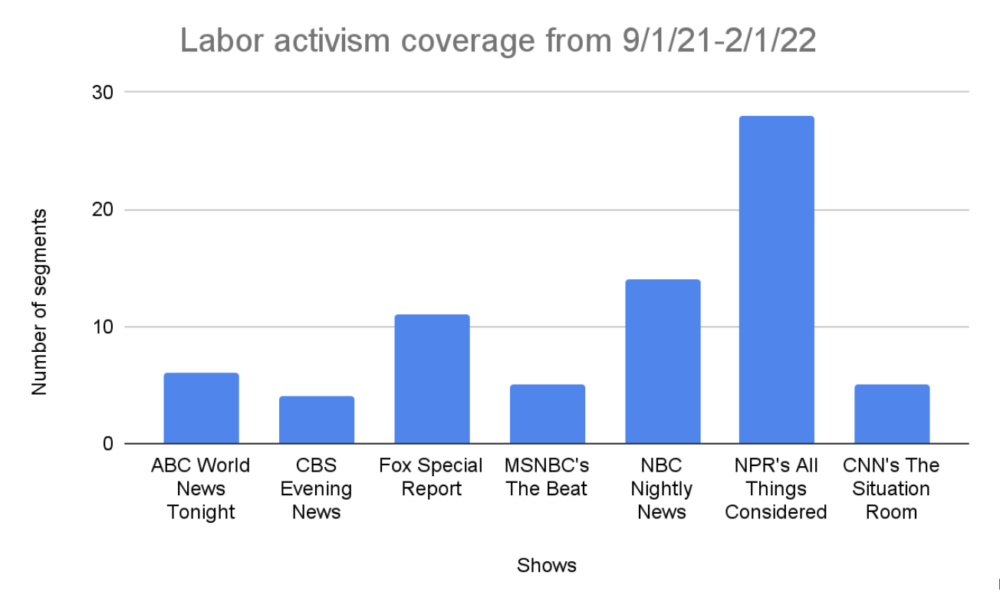
The Crowd Counting Consortium, founded in 2017 to collect “publicly available data on political crowds reported in the United States,” tracked more than 2,000 protests in February alone.
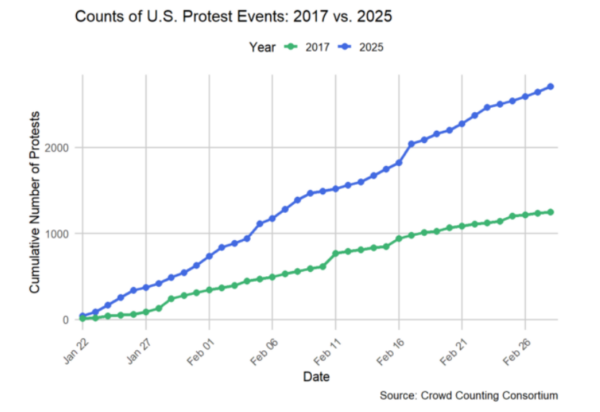
Chart: Waging Nonviolence
The acts of collective resistance documented by the CCC—as well as by other activism-tracking initiatives, such the “We the People Dissent” Substack—span every state. They focus on advocacy for diverse constituencies and issues under attack from the current administration, including public education, Medicaid and reproductive, immigrant, Palestinian, labor and LGBTQ rights.
Their common thread is opposition to Trump’s fascistic ideology and rapid rash of likely unconstitutional executive orders, such as freezing federal budget outlays approved by Congress, the mass firing of government workers and the dismantling of institutions by the “Department” of Government Efficiency by unelected “adviser” Elon Musk.
But if you relied on articles and broadcasts from the legacy national news media during early 2025, you wouldn’t know the extent of grassroots action prompted by this discontent. A FAIR examination of five major outlets found that coverage of anti-Trump/pro-democracy protests roughly overlapping CCC’s study timeframe (January 22 to February 26) was minimal, and downplayed the significance of this opposition, especially around the inauguration.
Mostly tepid coverage
FAIR examined reporting on three organized protest events occurring concurrently in Washington, DC, and across the US: The People’s March (January 18), the “50501” demonstrations in all state capitals (February 5) and the Presidents Day protests, sometimes dubbed “No Kings Day” (February 17). Using the Nexis news database and the outlets’ websites, we looked at the New York Times, Washington Post and USA Today, and at ABC World News Tonight, Good Morning America, CBS Evening News and CBS Mornings—the top morning and evening national news programs on ABC and CBS—within four days of each of these dates. (NBC was not included in the study because its transcripts are no longer available on Nexis.)
Broadcast coverage was abysmal. None of the four network shows in our study ran any reports focused on any of the three protest events. ABC World News Tonight mentioned none of the events, and GMA referred to only one of them in passing. In their coverage of the January 18 protests, CBS Evening News and Mornings gave more coverage to speculation about violent protest than they did to actual (nonviolent) protest.
The newspapers had more coverage, but their stories tended to be relatively short, buried deep in the paper, or in the form of wire-service reprints. Longer pieces often downplayed the protests’ size and disparaged their significance. The Times and Post tended to focus on DC-based protests, whereas USA Today offered more thorough and accurate articles about the growing nationwide resistance movement.
The People’s March
The January 18 march, centered in Washington, DC, near Inauguration Day, was a reboot of the attendance record–setting 2017 Women’s March spearheaded by feminist nonprofits. The People’s March had a broadened focus on peaceful organizing around a range of progressive issues, and included solidarity actions in every state.
According to CCC data (available for download at the site), on January 18 alone, 352 protests, rallies, demonstrations or marches opposing Donald Trump and/or administration policy were recorded across the country. Though dispersed in a way the Women’s March was not, tens of thousands nonetheless participated in hundreds of acts of protest and civil disobedience around the country.
More than 200 additional on-the-street actions occurred on January 19–20, many linked to Martin Luther King Jr. Day, but also including messages against Trump’s agenda, according to CCC data.
We found no mention of any of the People’s Marches on the ABC shows in our study, and no dedicated stories about the protests on the CBS shows we examined. In two segments focused on the incoming administration, CBS mentioned protests generically, only in passing, and focusing solely on those in the nation’s capital.
After noting that “today, thousands of people could be seen protesting the president-elect in Washington, DC,” reporter Jericka Duncan (CBS Evening News, 1/18/25) devoted more time to security measures around potential “violent protests”—a concern repeated in a January 20 segment on CBS Mornings (1/20/25).
‘Accommodation and submission’

New York Times (1/19/25)
The newspapers studied all covered the People’s Protests, but the Times and Post downplayed their significance. The Times (1/18/25) published “‘Angry and Frustrated’: Thousands Protest Trump Days Before His Inauguration,” a thousand-word story that captured the mood and nationwide extent of concern expressed by the events, but made a point of noting that the DC march “paled in comparison to the Women’s March.” It was buried on page A25.
The following day, the Times published a longer (1,600-word) piece on how “The Trump Resistance Won’t Be Putting on ‘Pussy Hats’ This Time,” based on interviews with middle-American activists. The article alleged that “the Democrats who mobilized against Donald J. Trump in 2017 feel differently about protesting his return,” by which they meant defeated and ambivalent. It asserted that “there are few signs of the sort of mass public protest that birthed ‘the resistance’ the last time [Trump] took office.”
There was also a 1,600-word Washington Memo (1/19/25) headlined “Defiance Is Out, Deference Is In: Trump Returns to a Different Washington”:
Unlike the last time President-elect Donald J. Trump took the oath of office eight years ago, the bristling tension and angry defiance have given way to accommodation and submission. The Resistance of 2017 has faded into the Resignation of 2025.
Washington Post (1/17/25)
The Washington Post had two pieces. The predictive “How Resistance to Trump May Look Different in His Second Administration” (1/17/25) came in at around 1,800 words, while the paper gave coverage of the actual DC event, “People’s March Protests Trump” (1/19/25), only 1,400 words. Both were by Ellie Silverman, its dedicated activism and protest movements reporter.
Like the Times’ articles, the former piece was focused on dispirited activists and how the resistance supposedly ain’t what it used to be. It described a “feeling of resignation in the lead-up to Trump’s second administration [that] is a stark departure from 2017, when more than 1 million people took to the streets.” It added that “some demonstrators are sticking to the sidelines,” and warned that some experts “fear that whatever protests do emerge could be even more disruptive and potentially violent.”
The straightforward latter story was more nuanced, focused on interviews with protesters on the diverse issues that brought them there, who maintained that showing up was more important than rally size. However, it didn’t mention that the protest was part of a larger, nationwide mobilization.
USA Today‘s piece on the People’s March (“Thousands Travel to Washington for People’s March Ahead of Trump Inauguration,” 1/18/25), like those of the other papers, covered only the DC demonstration, and dwelt on its smaller-than-2017 size. But it also portrayed fired-up citizens who made a point of being there to take a stand, rather than trying to tell a story of, as the Times said, “accommodation and submission.”
The 50501 protests
The 50501 protests, short for “50 protests, 50 states, one day,” were the brainchild of grassroots activists on Reddit wanting to take “rapid response” political actions against Trump and Project 2025, the right-wing blueprint for overhauling the federal government Trump and Musk seem to be following. Using mainly social media and the hashtags #BuildTheResistance and #50501, the organizers spurred others to organize and publicize demonstrations in all US state capitals on February 5. According to CCC data, some 159 “50501” or related protests occurred that day (exclusive of counter-protests), from Sacramento, Calif., to Augusta, Maine.
We found no coverage of the 50501 protests in the Washington Post, or on the CBS or ABC shows.
In its sole article, “Thousands Across the US Protest Trump Policies,” the New York Times (2/5/25) devoted only about 600 words to the nationwide rallies. Sara Ruberg’s story accurately portrayed them as “a grassroots effort to kick off a national movement,” quoting a Michigan state representative: “This was organized by people, for people, for the protection of all people…. There will be…more things for regular everyday Americans to plug into.” However, Ruberg depicted the decentralized, quickly organized efforts as something not to take too seriously:
Whether the protests will amount to a sustained anti-Trump movement is yet to be seen.
In the weeks following the election, Democrats were not able to come together under a single message as they did after the 2016 election, when Mr. Trump won the first time. Even the grassroots efforts that once organized large national marches and protests after Mr. Trump’s first inauguration have struggled to unite again.
The piece also said the events only occurred in “a dozen states”; CCC data confirms organizers’ claims that they spanned all 50 states, plus DC. An additional 1:20-minute video of protesters chanting appeared in the online version of this story, featuring passionate slogans like “Stand up, fight back,” “Stop the coup!” and “Impeach Trump” that belie the notion that activists have no uniting message.
USA Today (2/5/25)
At 2,500 words, USA Today‘s feature (2/5/25) on the 50501 demos, “‘People Are Feeling Galvanized’: Anti-Trump Protesters Rally in Cities Across US,” was by far the longest and most thorough of any in the study periods. Its lead set the protests in a broader context:
Groups opposed to actions by the Trump administration in recent weeks converged on cities Wednesday across the US to loudly register their discontent, days after widespread rallies and street marches against President Donald Trump’s immigration policies.
Integrating reporting from DC and 10 other capitals and cities (Austin, Salem, Indianapolis, Harrisburg, Des Moines, Columbus, Denver, Detroit, Palm Springs, Calif., and Greenville, S.C.), reporters John Bacon, Karissa Waddick and Jorge L. Ortiz discussed the major concerns of residents in each place, provided background on 50501 and Project 2025, and quoted marginalized people targeted by Trump, such as a trans woman and a refugee from Azerbaijan, along with supportive politicians and the AFL-CIO. The comments included captured the sense of seriousness and commitment of the rallies. It quoted 70-year-old Stewart Rabitz:
“I think a lot of people are now realizing that walking around with signs, people got to get their hands dirty.”… Asked whether he feared retribution, Rabitz said: “You can’t be afraid. I’m willing to be the first one. I’ll be the Tiananmen tank guy.”
No Kings Day

GMA (2/18/25)
The 50501 movement also spearheaded nationwide events, some dubbed “No Kings Day,” less than two weeks later, on February 17, to protest Trump’s undemocratic actions and monarchical leadership, coinciding with Presidents’ Day. The CCC tracked 207 such actions on February 17 (excluding a few counter-protests).
Once again, CBS and ABC had no reports focused on the protests. CBS gave them one sentence on CBS Mornings (2/18/25), which led with the controversy surrounding DOGE’s access to private information: “Protests called ‘No Kings on Presidents’ Day’ against Musk and President Trump’s actions were held across the country yesterday, including outside the US Capitol.” ABC (GMA, 2/18/25), too, briefly mentioned “protests popping up in cities across the country,” even including short clips of protest footage—but also used the demonstrations as a brief segue to discuss DOGE cuts and access to sensitive data.
New York Times coverage included one story (2/17/25), provocatively titled “Thousands Gather on Presidents’ Day to Call Trump a Tyrant.” It focused on the DC march, but did give a sense of the nationwide sweep of actions, noting that protestors framed themselves as patriots fighting tyranny. The piece acknowledged that while
Democratic leaders and operatives [are] worried about alienating voters in reacting hastily without reflecting first on why they lost in 2024. Many activists…have voiced frustration at the lack of a more aggressive stance.
The piece, however, was buried on page A18.
For its part, the Post devoted only one 500-word AP dispatch (2/17/25) to the events, “‘No Kings on Presidents Day’ Rings Out From Protests Against Trump and Musk.” But the subhead did note, “Protesters against President Donald Trump and his policies organized demonstrations in all 50 states for the second time in two weeks.”
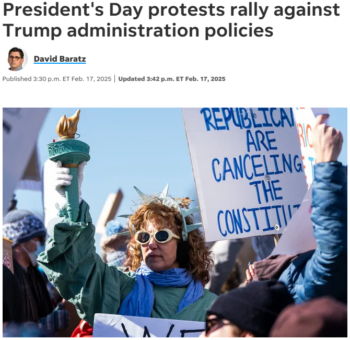
USA Today (2/17/25)
USA Today published a photo gallery (2/17/25) and a 900-word story (2/17/25) about the Presidents’ Day protests, focused more on regional actions that “swept across the nation” than on DC. Providing important context, “‘Critical Moment in History’: Protests Across US Target Trump, Musk” (2/17/25) led with this:
Groups opposed to President Donald Trump’s agenda and his top adviser Elon Musk converged on cities across the nation Monday to express outrage with slogans such as “Not My President’s Day” and “No King’s Day.”
The rallies, led by the 50501 Movement and other organizations, come less than two weeks after the last round of widespread rallies and street marches.
This broader perspective on the resistance demonstrations may be thanks to the middle-of-the-road paper’s less-insular focus: It covers all 50 states, serves a more diverse audience, and utilizes reporting from its partner papers across the country.
Another mass mobilization
On April 5, yet another grassroots, mass mobilization—organized around the taglines “Hands Off” and “People’s Veto”—is planned for the streets of DC and across all 50 states. Will the legacy media be there and give it the broad and contextualized coverage it deserves? Will they more proactively cover the increasingly localized demonstrations and other forms of political participation—or leave that task to the rapidly shrinking pool of local and regional news outlets? For if CCC’s data is accurate (and it may be an undercount), the nascent pro-democracy movement deserves its own dedicated beat.
Research assistance: Wilson Korik
This post was originally published on FAIR.


 The murder of UnitedHealth Group executive Brian Thompson, and the subsequent arrest of Luigi Mangione, focused media and policymakers’ attention on the savage practices of private US health insurance. In the immediate
The murder of UnitedHealth Group executive Brian Thompson, and the subsequent arrest of Luigi Mangione, focused media and policymakers’ attention on the savage practices of private US health insurance. In the immediate 









 With less than a month until Election Day, Democratic presidential nominee Kamala Harris and her running mate, Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, sat down for an interview with Bill Whitaker on CBS‘s 60 Minutes (
With less than a month until Election Day, Democratic presidential nominee Kamala Harris and her running mate, Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz, sat down for an interview with Bill Whitaker on CBS‘s 60 Minutes (