By David Robie, convenor of Pacific Media Watch
Along with the devastating death toll – now almost 35,000 people, hundreds of aid workers and hundreds of medical staff have been killed in the genocidal Israeli war on Gaza — journalists have also paid a terrible price.
By far the worst of any war.
In Vietnam, 63 journalists were killed in two decades.
- READ MORE: Auckland Palestine rally honours Gaza journalists for freedom award
- Netanyahu government votes to close Al Jazeera channel in Israel
- Other War on Gaza reports
The Second World War was worse, with 67 journalists killed in seven years.
But now in the war on Gaza, we have had 143 journalists killed in seven months.
That’s the death toll according to Al Jazeera and the Gaza Media Office. (Western media freedom monitoring usually cite a lower figure, around the 100 plus mark, but I the higher figure is more accurate).
And these journalists — sometimes their whole families as well – have been deliberately targeted by the Israeli “Offensive” Force – I call it “offensive” rather than what it claims to be, defensive (IDF).
Kill off journalists
Assassination by design. Clearly the Israeli policy has been to kill off the journalists, silence the messengers, whenever they can.
Try to stifle the truth getting out about their war crimes, their crimes against humanity.
But it has failed. Just like the humanity of the people of Gaza has inspired the world, so have the journalists.
Their commitment to truth and justice and to telling the world their horrendous story has been an exemplary tale of bravery and courage in the face of unspeakable horror.
But there has been a glimmer of hope in spite of the gloom. On Friday — on World Press Freedom Day, May 3 — UNESCO, the United Nations cultural agency, awarded all Palestinian journalists covering the war in Gaza the annual Guillermo Cano Award for media freedom.
This award is named in honour of Guillermo Cano Isaza, a Colombian investigative journalist who was assassinated in front of the offices of his newspaper El Espectador in Bogotá, Colombia on 17 December 1986.
Announcing the Gaza award in the capital of Chile, Santiago, in an incredibly emotional ceremony, Mauricio Weibel, chair of the international jury of media professionals, declared:
“In these times of darkness and hopelessness, we wish to share a strong message of solidarity and recognition to those Palestinian journalists who are covering this crisis in such dramatic circumstances.
“As humanity, we have a huge debt to their courage and commitment to freedom of expression.”
Ultimate price
For those of us who watch Al Jazeera every day to keep up with developments in Palestine and around the world — and thank goodness we have had that on Freeview to balance the pathetic New Zealand media coverage — I would like to acknowledge some of their journalists who have paid the ultimate price.
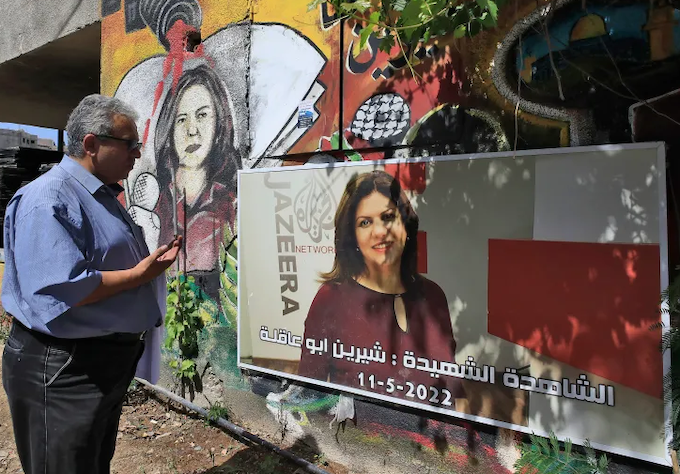
First, I would like to acknowledge the assassination of American-Palestinian Shireen Abu Akleh, who was murdered by Israeli military sniper while reporting on an army raid on the Jenin refugee camp in the West Bank on 11 May 2022.

A year later there was still no justice, and the Paris-based media freedom watchdog Reporters Without Borders issued a protest, saying:
“The systematic Israeli impunity is outrageous and cannot continue.”
Well it did, right until the war on Gaza began five months later.
But I am citing this here and now because Shireen’s sacrifice has been a personal influence on me, and inspired me to take a closer look into Israel’s history of impunity over the killing of journalists — and just about every other crime. (It has violated 62 United Nations resolutions without consequences).
I have this photo of her on display in my office, thanks to the Palestinian Youth Aotearoa, and she constantly reminds me of the cruelty and lies of the Israeli regime.
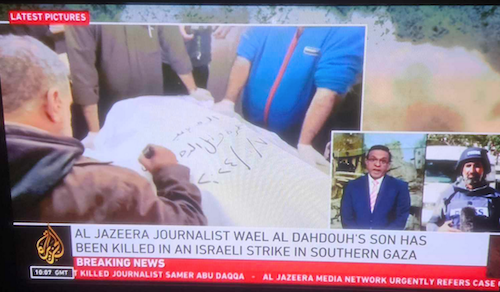
Now moving to the present war, last December, Al Jazeera’s Gaza bureau chief Wael Dahdouh was wounded in an Israeli strike in which his colleague and Al Jazeera Arabic’s cameraman Samer Abudaqa was killed, while they were reporting in southern Gaza.
Dahdouh’s wife Amna, son Mahmoud, daughter Sham and grandson Adam were previously killed in an attack in October after an Israeli air raid hit the home they were sheltering in at the Nuseirat refugee camp.
Then the veteran journalist’s eldest son, Hamza Dahdouh, also an Al Jazeera journalist, was killed in January by an Israeli missile attack in Khan Younis, southern Gaza.
News media reports said he was in a vehicle near al-Mawasi, an Israel-designated safe area, with journalist Mustafa Thuraya, who was also killed in the attack.
According to reports from Al Jazeera correspondents, their vehicle was targeted as they were trying to interview civilians displaced by previous bombings.
In February, Mohamed Yaghi, a freelance photojournalist who worked with multiple media outlets, including Al Jazeera, was also killed in an Israeli air strike in Deir el-Balah, central Gaza.
Al Jazeera’s Gaza offices in a multistoreyed building were bombed two years ago, just as many Palestinian media offices have been systematically destroyed by the Israelis in the current war.
Israeli PM Benjamin Netanyahu’s cabinet has voted unanimously to close Al Jazeera’s operations in Israel.
Vote comes after the Knesset passed a law allowing the temporary closure of foreign broadcasters considered a threat to national security
pic.twitter.com/zFDPQdowXG
— Al Jazeera English (@AJEnglish) May 5, 2024
Last month, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu branded Al Jazeera as a “terrorist channel”. Why? Because it broadcasts the truth about Israel’s genocidal war and Netanyahu threatened to ban the channel from Israel under a new law to control foreign media.
Today, a month after that threat, Netanyahu has today followed up after his cabinet voted unanimously to order Al Jazeera to close down operations in Israel, which will curb the channel’s reporting on the daily Israeli harassment and raids on the Palestinians of the Occupied West Bank.
And this is the country that proclaims itself to be the “only democracy” in the Middle East.
Many of the surviving Gaza journalists are very young with limited professional experience.
They have had to learn fast, a baptism by fire.
I would like to round off with a quote from one of these young journalists, Hind Khoudary, a 28-year-old reporter for Al Jazeera since day one of the war, who used to sign on her social media reports for the day “I’m still alive”:
“I am a daughter, a sister to eight brothers, and a wife.
“Choosing to stay here is a choice to witness and report on the unbearable reality my city endures. Forced from my home, alongside countless Palestinians, we strive for the basics – clean food and water – without transportation or electricity.
“I am not a superhero; I am shattered from the inside. The loss of relatives, friends, and colleagues weighs heavy on my soul. Israeli forces ravaged my city, reducing homes to rubble. [Thousands of] civilians still lie beneath the remnants.
“My heart is aching, and my spirit is fragile. Since October 7, journalists have been targets; Israel seeks to stifle our voices.
“I miss my family.
“But surrender is not an option. I will continue to report, to breathe life into the stories of my people until my last breath. Please, do not let the world forget Palestine. We are weary, and your voice is our strength.
“Remember our voices, remember our faces.”

This article is adapted from a media freedom speech by Pacific Media Watch convenor Dr David Robie at the Palestine rally today calling for an immediate ceasefire in the Gaza war.
This post was originally published on Asia Pacific Report.











 “The clue is in the name: ‘Lawyers for Israel’ thought that they could run a campaign to bully an ABC journalist out of her job —…
“The clue is in the name: ‘Lawyers for Israel’ thought that they could run a campaign to bully an ABC journalist out of her job —…