The vision
“After the ninth epidemic of mad cow disease, everyone was already eating insects. So we weren’t the first restaurant in PuertoChina to do it,” said Nai Nai.
Nai Nai often told these stories while she and Grace squatted in a corner of the kitchen, soaking the cocoons in steaming hot water. Grace always liked to stir the paddle, loosening any stray dirt or leaf debris off the floating swaddled worms. It was Nai Nai’s role to take the washed cocoons, and with a deft hand and a sharp knife, pluck out the plump meat inside. Clean and quick.
“But no one,” said Nai Nai, finally getting to the part Grace liked best, “no one was serving silkworm on Canal Street. Not until I opened up the first restaurant! And they couldn’t get enough of it. I got the idea when I was walking past Mulberry. The city was planting more trees, and I thought, ‘You know, there used to be mulberry trees on Mulberry Street. Why don’t we bring them back?’”
— a passage from “The Ones Left Behind,” by K.J. Chien
The spotlight
Lobster was not always the luxury seafood that it is today. Before the late-1800s, the creepy-looking, bottom-feeding shellfish were super abundant on the northeast coast of the newly formed United States — they were cheap and generally viewed as a food for the poor, frequently fed to indentured servants and incarcerated people. But with the spread of railroads across the country, chefs began offering them to wealthy train passengers who weren’t aware of this reputation. They also discovered the still-used technique of boiling the creatures alive, which made the resulting dish more appetizing and aesthetically pleasing (if less humane). As more people discovered their deliciousness, lobsters became chic.
In the past decade or so, food startups and sustainability advocates have been hoping that a similar glow-up might be possible for other edible arthropods: insects.
Insect protein has been touted as the food of the future. Bugs are nutrient-dense and resource-efficient — farming insects uses only a fraction of the land and energy it takes to raise large mammals, and is generally thought to be more humane, because it’s easier to mimic the natural conditions that insects enjoy in the wild. And, as a bonus, they don’t burp out methane.
In “The Ones Left Behind,” a winning story in Grist’s latest Imagine 2200 climate short story contest, author K.J. Chien envisions a future where insect-eating has been embraced by the Western world. The story takes place in New York City, and centers around the main character’s family Sichuan restaurant — the signature dish of which is silkworms, raised onsite. (Hyper-local!)
“I was thinking of how climate change will disrupt crops and food supply chains, and was wondering how local communities might respond to that,” Chien shared in an email. She added that she chose to set the story in Chinatown (renamed “PuertoChina”) because of the history of discrimination against Chinese people and cuisine in the U.S. “I wanted to play with the idea of ‘disgusting’ alternative food sources, born out of climate change necessity, and subvert the trope by making it delicious.”
In one passage, Chien shows Grace, the main character, frying up a batch of pupae with ramps, red chili pepper, spicebush leaves, and wild ginger, and serving it to a friend for lunch: “Quique immediately drowned his dish in hot sauce; Grace bit into a crunchy shell, savoring the meat’s firm, creamy, and nutty bite underneath. It might’ve been Grace’s best batch yet, she thought. Quique’s fork, furiously scraping against his bowl, sang in agreement.”
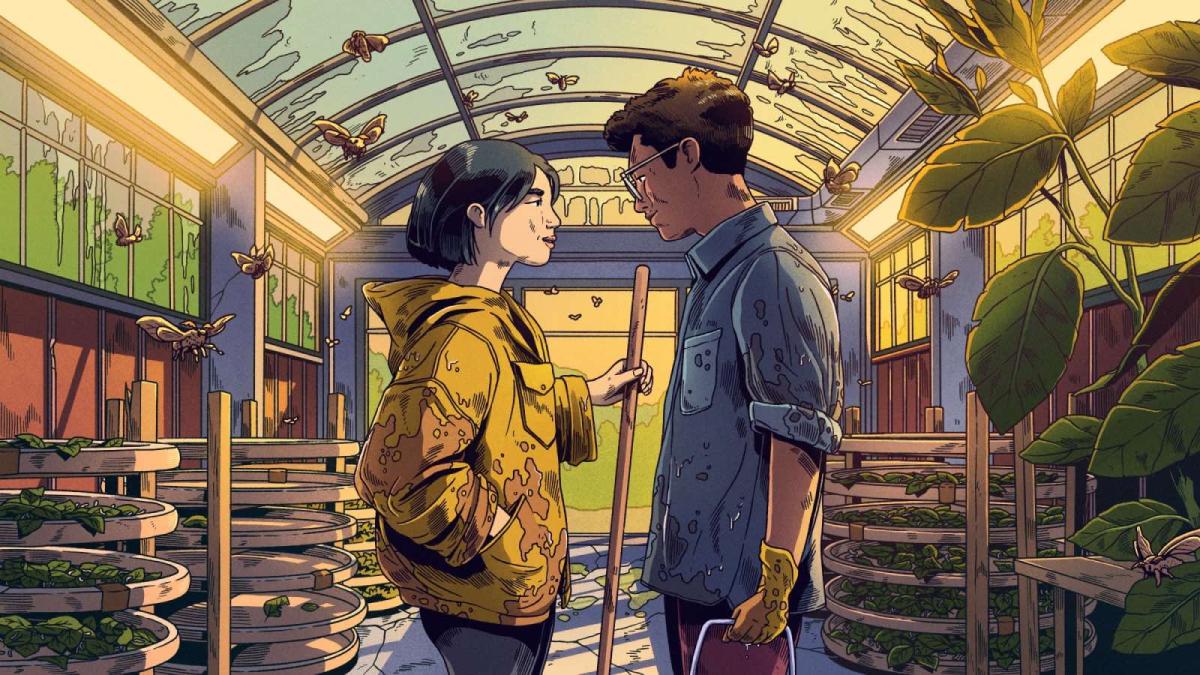

The lead artwork from “The Ones Left Behind,” showing the two main characters in the silkworm nursery in the back of Grace’s restaurant. Stefan Große Halbuer
According to many studies, averting catastrophic climate change will depend in part on wealthy countries drastically cutting back the amount of meat — especially beef — they’re currently consuming. Companies like Impossible Foods and Beyond Meat have tried to stake their claim (and largely fallen short) at getting meat lovers to switch to plant-based proteins that mimic the taste and texture of animal products. Could insects offer a more intriguing alternative — a way to continue eating from the animal kingdom without overextending the planet’s resources? It all depends on whether forces combine to get Western consumers over their learned disgust, something experts say is a tough bar to clear, but not an impossible one.
Disgust is cultural
Insects are already a food source for some 2 billion people all over the world, and have been for millennia. The fact that most people in Western countries don’t eat them today (and are generally repulsed by them) may have something to do with the fact that we live farther from the tropics — in colder regions, insects are smaller and less a part of daily life. The built environment that keeps us safe from the cold also keeps bugs out, contributing to this idea that we don’t want creepy-crawly things near us. But that perception might also have a lot to do with racism.
“The European habit of going to other places and colonizing them and othering their foods and calling them barbarians had a big impact on insects losing out of our traditions,” said Robert Nathan Allen, founding chair and current board member of the North American Coalition for Insect Agriculture.
Purposefully denigrating or mocking the culinary traditions of other cultures, including Native peoples in the Americas, who ate many types of insects, has been one tool used to justify things like colonization, forced assimilation, and xenophobia. Those negative associations that paint insect-eating as backwards or barbaric still persist in our media, even though their origins may be less obvious.
When Allen first got interested in insect cuisine over a decade ago, “the most common sort of cultural touch point to the idea of eating bugs was Fear Factor or Survivor,” he said.
But understanding how the history feeds into our perceptions today might be part of the key to changing attitudes. Because although disgust might feel very visceral, it can be reprogrammed. As anthropologist Julie Lesnik told Grist in May, “Disgust is one of the few learned emotions. So we are disgusted by the things our culture tells us to be disgusted by.”
In 2012, there wasn’t a lot of information to be found online about farming and eating insects, Allen said, beyond dense academic journals. Undeterred, he began growing his own mealworms and processing them into cookies that he took to farmers markets in Austin, Texas, to see what other people thought of the idea. “Most adults had a cultural, psychological taboo that was entrenched — but kids were so, so receptive, especially younger children,” he said.
Seeing a need for education about the goodness of edible insects, he helped organize conferences, an annual bug eating festival in Austin, and a series of future-of-food events at the media and culture festival South by Southwest. Those events have been fruitful, he said, and the idea of edible insects in the U.S. — as well as a handful of reasonably successful products — has been around for a while now. “There’s certainly lots of restaurants that serve them on the menus, and there are more chefs I think now than there were 10 years ago that are interested in experimenting with them,” he said. But thus far, insects have failed to capture the imaginations of American eaters and producers in a major way. “It just hasn’t hit any sort of tipping point.”
Food is political
Whether insects can hit that tipping point and change their place in Western culture, like the lobster more than a century ago, is a question tied in with so many of the other culture battles playing out in our society. While some consumers might seek out an insect protein bar because they’ve heard it’s the sustainable food of the future, others might avoid it for the exact same reasons.
“When you have all the breadth of choice of food, your choices matter a lot more in your self-identification and your actualization within a political, social world,” said Soleil Ho, a food and culture writer for the San Francisco Chronicle, and former chef, podcast host, and restaurant critic. They emphasized that the foods we choose to eat are an important part of how we create our sense of identity, and even how we express our political worldviews — and right now, that might not be playing in the favor of overcoming cultural disgust around eating insects.
“We’re in this moment where the right wing of politics in the United States, and even Western Europe, are positioning insects as what the left wants you to eat. You’ve seen that in the sort of fake culture war rhetoric about Kamala Harris taking away your right to eat a cheeseburger,” they said. The notion that Kamala Harris wanted to ban red meat was false, and so is the conspiracy theory that leftist governments (or billionaire Bill Gates) want to force people to eat insects. Nevertheless, those sensationalized claims have seemed to galvanize some people even further against the idea — creating yet another layer of cultural resistance.
In our current political climate, Ho is pessimistic about the likelihood that insects will endear themselves to an American audience the way that other novel foods, like sushi, have managed to do in the past.
Although, they added, insects have gained a foothold in our food system in other ways that many people can’t see. They’ve become increasingly common as feed for livestock, and an ingredient in pet food and treats.
Allen is more hopeful that the growth of those industries will be a part of paving the way for insects to creep more and more into people’s diets, too. “As they become cheaper, and can be grown in more volume because of the scale for those industries, it’ll make it a lot easier for chefs and consumer product-makers to start using them,” he said. And, he added, chefs will likely play a huge role in exposing people to these new ingredients in compelling and creative ways.
“Here in Austin, there are multiple restaurants that do a great job of that,” he said. “They create dishes that allow people to try the insects in a way that is enjoyable instead of sensational — it incorporates it into a delicious dish the same way that you would a watermelon radish or, you know, any other weird thing that is a new ingredient that someone’s never heard of.”
If he had to choose a gateway bug that could get Americans hooked on the idea of eating insects, his nominee would be grasshoppers. They’re large, visually interesting, and incredibly high in protein, all of which could make them a culinary winner. Although, he added, black soldier fly larvae offer an example of a bug that’s currently being farmed for animal feed, but could cross over into human diets. “They have a really high fat profile, so they’re supposed to taste delicious,” he said. He plans to experiment with them in 2025.
Ho similarly expressed that focusing on the unique attributes of specific insects, and the wonderful dishes they can be a part of — like the Sichuan silkworms in Chien’s short story — will likely present a more compelling entry point for most people than the broad idea of eating insects for the sake of eating insects.
They also added that our innate interest in tasty bugs might not be as deeply buried as some people’s gut reactions would suggest. “I’ve heard from a lot of people, who are not interested in insects, that the grubs from The Lion King were the most delicious movie food they’ve ever seen,” Ho said. “We’re all human beings. Probably most of us have descended from bug lovers. So it’s in there still, the desire.”
— Claire Elise Thompson
More exposure
A parting shot
H Mart, the largest Asian grocery store chain in the U.S., just opened its newest location earlier this month in Somerville, Massachusetts. And one of the offerings on the shelves: packaged silkworm pupae in sauce!

IMAGE CREDITS
Vision: Grist
Spotlight: Stefan Große Halbuer
Parting shot: Lane Turner / The Boston Globe via Getty Images
This story was originally published by Grist with the headline Fiction to reality: Will the U.S. ever embrace insect cuisine? on Jan 15, 2025.
This content originally appeared on Grist and was authored by Claire Elise Thompson.
This post was originally published on Radio Free.








